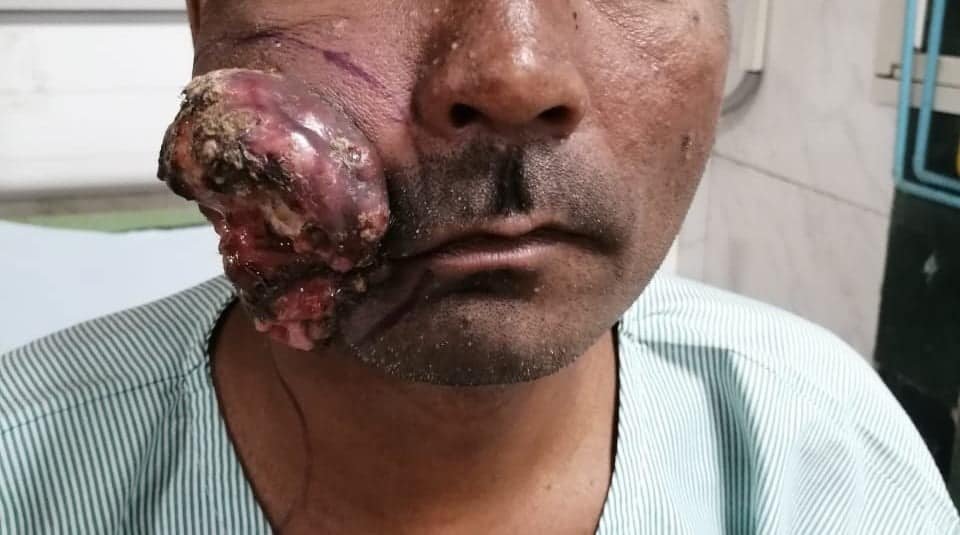
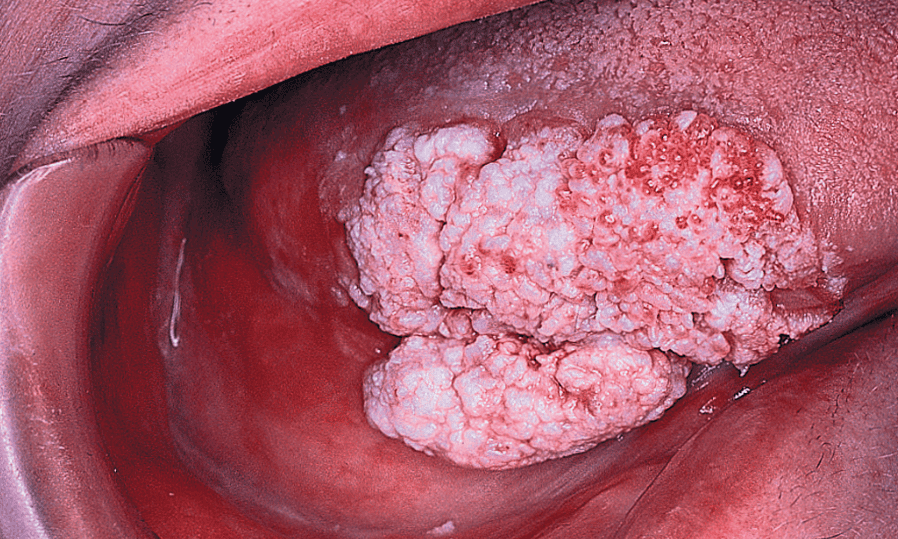
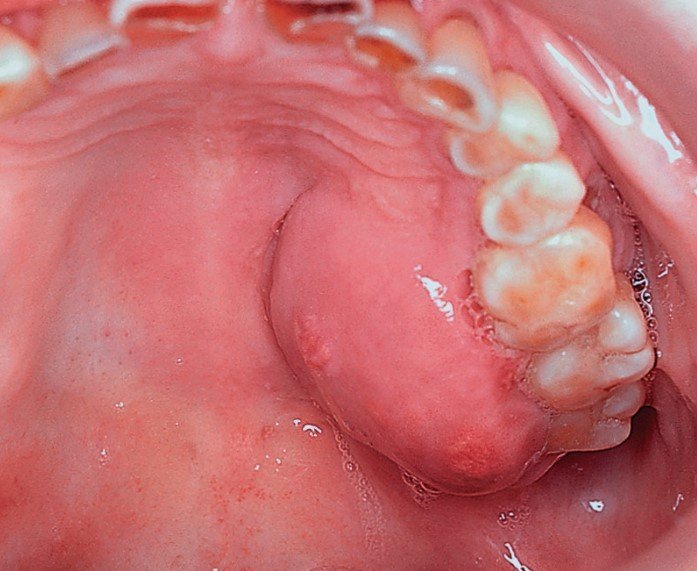
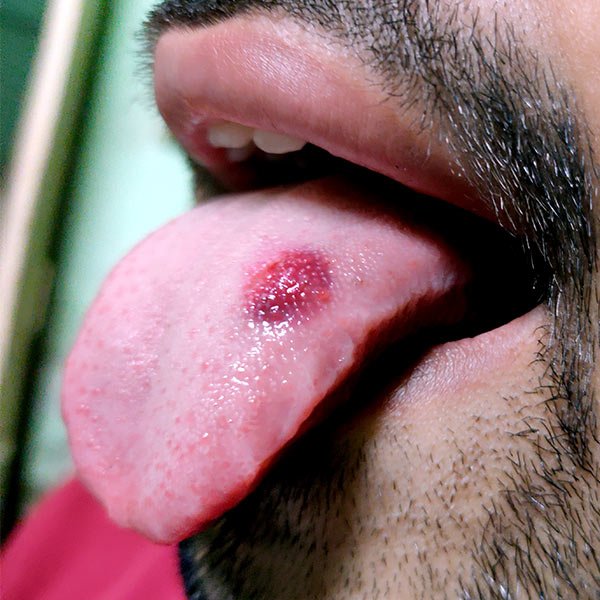
Main modality of treatment is surgery, potentiated by radiation therapy in locally advanced cases.
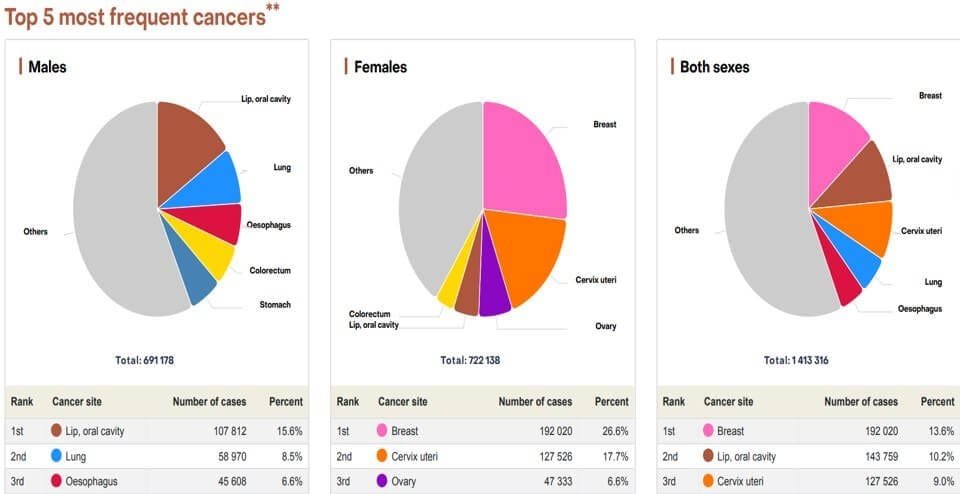
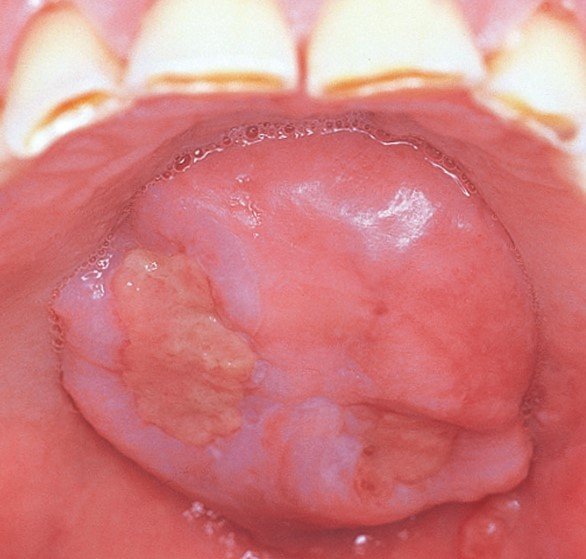
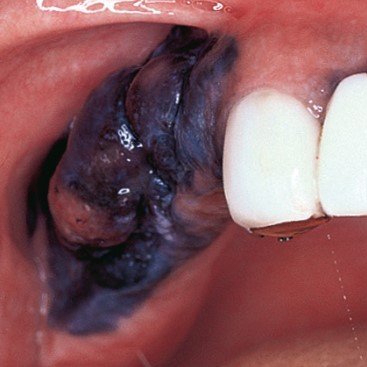
Oral cancer, additionally referred to as mouth cancer, is commonest amongst the head and neck cancers. As per statistics, carcinoma develops in 10.5 adults per one 100,000 population. The foremost common causes embrace a mixture of excessive smoking and alcoholic abuse. The commonest sign of developing carcinoma is ulceration that doesn’t heal within a fortnight. The key to successfully treat carcinoma is its timely detection and treatment.